How and Why Telecommunication Companies Use Big Data

IT copywriter
Reading time: 11 min
Have you ever received a retail coupon that reflected a recent purchase, or been sent a special offer via SMS from an establishment as you walked by it? Most likely you have, and the precision of retail advertising is no surprise these days. Typically, such deep knowledge of a customer is derived from a phone call and billing records, purchase history, payment records, GPS, etc. — or in other words, through the analysis of “Big Data”. Big data in telecom is a valuable tool applied to better serve the customer by analysing their activity and backgrounds.
But don’t take this the wrong way: Big Data telecom usage isn’t a threat to our privacy. Instead, this term refers to the exponential growth and availability of raw data. When this data is processed, it provides valuable business insights.
While a certain portion of Big Data telecom is relatively easy processes — e.g. the source data for retail projections mentioned above — other data is much less consistent and harder to obtain and analyze. This article focuses on BD and its benefits for telecommunication company owners. We will also examine a few potential hurdles of Big Data processing — and how to jump over them.
Firstly, let’s define key terminology.
What is Big Data?
Big data (BD), if explained simply, is a general term used to describe vast and unstructured data flow as well as technologies used to analyze and process it. Gartner provides a more complex definition, referring to it as “high-volume, high-velocity, and high-variety information assets that demand cost-effective, innovative forms of information processing for enhanced insight and decision making.”
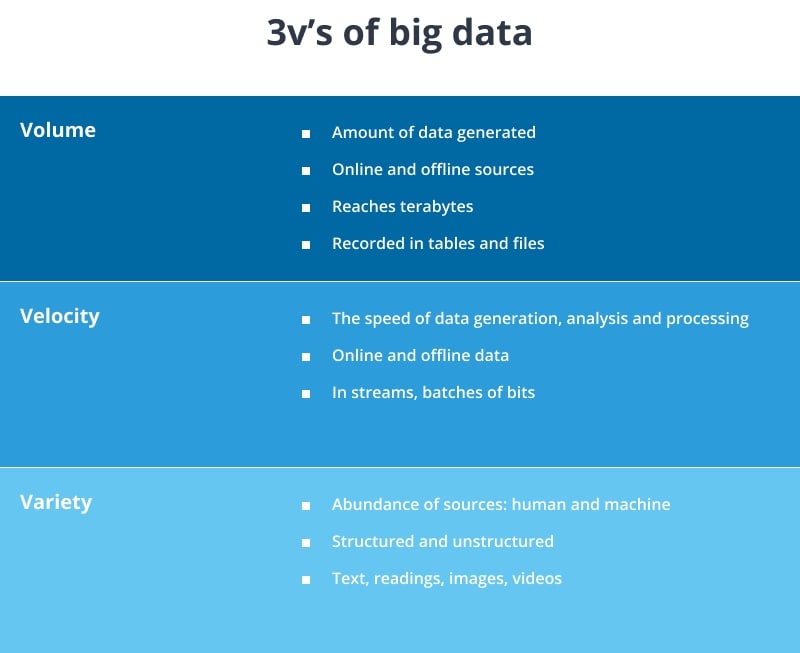
According to the Gartner definition, BD can be described using three “V’s”: volume, variety, and velocity.
Volume
Volume is the base BD is built on. Each day a gigantic amount of data is being produced by all sorts of sources. Techjury claims that 2.5 quintillion bytes of data is created worldwide every day. That’s a lot, though most of this data will never be processed.
Variety
This term relates to the diversity of data types and sources. Data comes from web pages, search engines, social media, data sensor systems, and it’s all raw, semi-structured or unstructured. In many ways it is a struggle for enterprises to turn this data mess into a coherent flow of information.
Velocity
Velocity refers to the enormous data generation, analysis and reprocess speed. Nowadays data spawns in a blink of an eye, and is hard for most companies to process.
Apart from three fundamental V’s, some sources also point out others:
- validity (veracity) – the quality of data and it’s authenticity;
- variability – the complexity of contexts one piece of data can have;
- visualization – how to properly represent large chunks of data;
- value – what profits can be drawn from the data analysis.
While these “V’s” are not so common in description of the subject, they add precision to the fundamental principles.
Why do telecommunication companies use Big Data?
The answer is that simple, really – to increase profits. Telecom networks are flooded with data so it is vital for the operators to take advantage of it. Properly utilizing Big Data analytics’ insights companies may optimize network usage, improve customer experience and enhance security. The potential of telecom Big Data analytics is significant in terms of winning the clients.
Big Data impact over telecom industry
Most telecom companies that adopted BD are early birds of this technology of turning data into profitable insights. According to IDG, only 20% of telecom companies have been deploying BD, while another 70% think that big telecom data is going to play a big role in the future of telecommunication business.
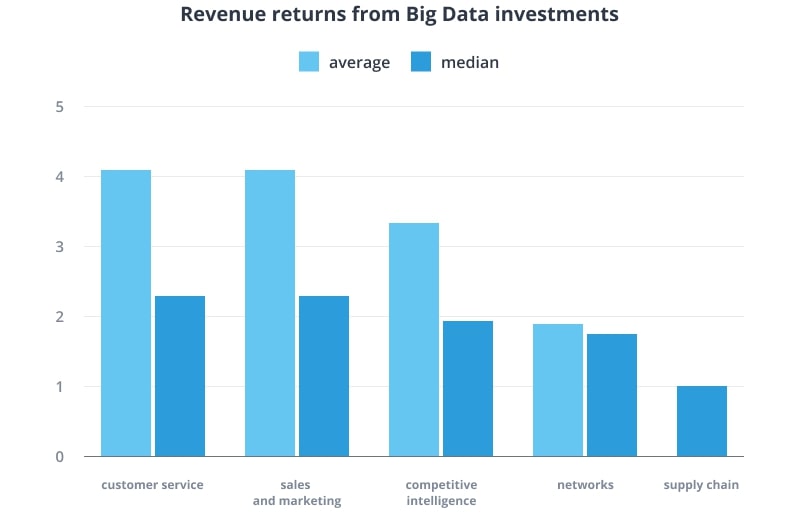
It’s not surprising why – there are lots of areas where companies may apply Big Data analytics. Projects are launched in sales and marketing, for customer care, competitive intelligence, network and supply chain optimization. Generally, customers provide competitive insights when facing these domains.
When it comes to profit, the returns of Big Data telecom investments are considerable. Average returns are a little less than 3%, but it also impacts around 6 percent of total company productivity. Revenue differs in domains:
Bughin, J. Reaping the benefits of BD in telecom. J Big Data 3, 14 (2016).
Precise statistics vary business to business. Nevertheless, such results should be considered good for a relatively new way of information handling.
Big Data usage in telecom industry
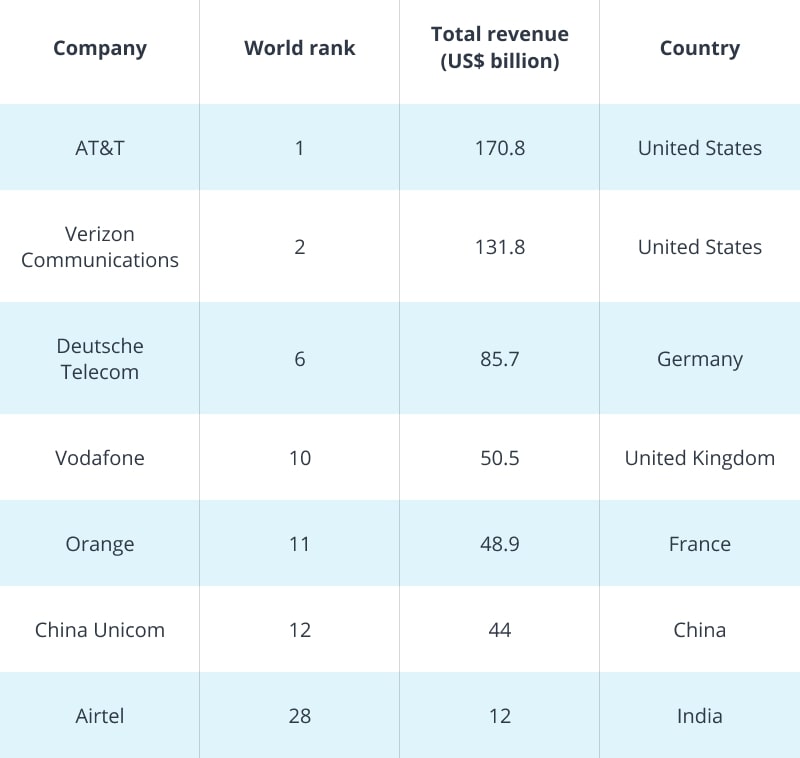
As it was mentioned above, for a small telecom company Big Data management is not simple to handle, it comes as no surprise that it is in profitable telecom companies where the telecom data analytics are applied. As you can see in a table below, there are a few major players all over the world that are successfully applying it in their telecom businesses:
There are also smaller companies that aren’t in a top-50 industry players, but still apply telecom data:
- Telkomsel – Indonesia
- Spark – New Zeland
- T-Mobile – US
- Ufone – Pakistan
- Safaricom – Kenya
Which proves that pretty much every company may take advantage of telecom data, no matter big or small.
Big Data telecom use cases
At the Telco event held in 2015, several companies shared a positive view on their BD experience:
- Guavus, a vendor of telecom-focused analytics software, reported that due to a better understanding of network utilization (insights were extracted from BD) a reduction in network equipment costs from $1B to $54M was achieved by one of their clients;
- Many CSPs claimed a doubling of product sales. BD provided material for more efficient targeting of their key markets.
- Sprint reported generating $10M in revenue through the external sale of marketing insight data on its customers, acquired with utilization of BD.
As you can see, Big Data for telecom is not only a valuable insight provider, but a subject for monetization. To track data streams and enhance the quality of data major telecoms like Verizon also apply machine learning, as a potential automatization tool.
How do telecommunication companies use big data?
Now that we’ve discussed major big data telecom users, let’s examine how exactly it can be applied to business and what advantages it can bring.
Smarter traffic monitoring
Telecoms utilise enormous networks of thousands of devices running all the time. The BD tools help analyse network traffic in real time, identifying problems to fix them asap and predict peak loads to increase overall performance.
Pricing optimization and targeted campaigns
BD tracks various metrics in real time allowing to price the product and test it on customers of different segments and regions. Using big data for telecoms helps the company to come up with a price that suits both the company and the customers, ensuring steady income.
The same metrics help to understand what customers are likely to buy. Marketing campaigns, powered by BD, appear in the right place at the right time and contain the right message. Personalized products receive more clicks and way more appealing than random ads unrelated to customer needs.
Contextualized Promotions
BD helps to locate customers on a map in real time, compare their proximity to a closest promotion and send them, for example, a 20% off coupon at the nearest bookstore. Such promotions are of a higher conversion rate and bring revenue cut to telecom on each transaction.
Risk reduction
Toll number, bypass and credit card frauds may cost telecom companies a fortune. BD detects cloned sim-cards, unauthorized traffic and toll numbers and helps to take preventive measures against it.
Big Data in telecom: Customer case study
Our regular customer – one large Australian wireless operator – decided to take advantage of BD, but it would result in replacement of their entire IT system. Let’s see how our team turned this situation to a benefit for the client.
How it started
The major challenge was the absence of a single network storage point for the dispersed data: all network equipment and configuration information was processed by Cramer OSS Suite. The Azoft team discovered that to meet telecom industry demands our client had to move to a new version of Cramer.
This transition was the root of the problem. Since Cramer systems are highly customized and fine-tuned, the migration tools that allow quick data migration are practically nonexistent. Not to mention BD storages are enormous – so what data transfer tool will fit the telecom service company?
Solution
Our team held an extensive research of the market to procure an innovative migration tool that was the best fit to this project. The tool automated the migration process and helped to reduce downtime by taking advantage of the bi-directional synchronization of the source and target data.
Outcome
The project was a success, and our client was able to process Big Data to their benefit. If you are interested in applying big data to your business, consider contacting us to ensure your success.

Comments